FREQUENCY, WAVELENGTH & TIME PERIOD
In general, frequency, wavelength & time period are quite confusing parameters. Indeed, these three are entirely different in nature.
FREQUENCY
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. Unit of frequency is hertz(hz).
WAVELENGTH
Wavelength is the distance between identical points in the adjacent cycles of a waveform signal propagated in space or along a wire. Unit of wavelength is meter(m).
TIME PERIOD
The time taken to complete one full cycle is said to be time period. Unit of time period is meter/second (ms).
EXAMPLE
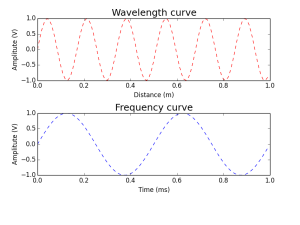
Lets take a signal at 2 kHz. Then the period is 0.5 ms. To plot this as a function of time.If a sound wave is travelling in space with a speed of 340 m/s then the wavelength is the distance the sound will travel in a period 340 * 0.5m = 17 cm. (i.e) 0.17m
PYTHON CODE
import numpy as n
import matplotlib.pyplot as p
f = 2
y = .17
d =n.arange(0,1,0.01)
t=n.arange(0,1,0.01)
wavelength =n.sin(2*n.pi/y*d)
frequency =n.sin(2*n.pi*f*t)
p.subplot(211)
p.plot(t, wavelength,’r–‘)
p.xlabel(‘Distance (m)’)
p.ylabel(‘Amplitute (V)’)
p.title(‘Wavelength curve’, fontsize=18)
p.subplot(212)
p.plot(d,frequency,’b–‘)
p.xlabel(‘Time (ms)’)
p.ylabel(‘Amplitute (V)’)
p.title(‘Frequency curve’, fontsize=18)
p.show(block=False)
WAVEFORM