FOURIER SERIES:
In mathematics, a Fourier series is a way to represent a wave-like function as the sum of simple sine waves. More formally, it decomposes any periodic function or periodic signal into the sum of a set of simple oscillating functions, namely sine and cosine with the harmonics of periods. So, Fourier series are used in the analysis of periodic functions.
Fourier Series:
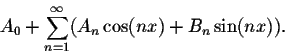
where,
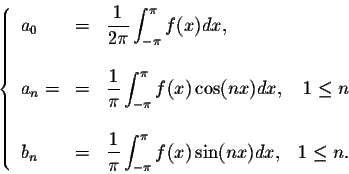
Here i used python programming tool instead of manual calculation to represent the Fourier
Series with some examples
.
PYTHON CODE:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
resolution = 0.0001
x = np.arange(-np.pi,np.pi,resolution)
square = np.array(x) ……
See more
OUTPUT WAVEFORM:


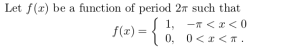
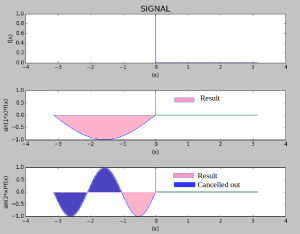
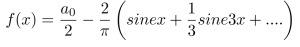
1) Naming consistency between A_n and a_n, B_n and b_n
2) Add comments to the python code
3) Waveforms needs to make more sense. Instead of calling it first harmonic can you say sin(1*x)*f(x).
4) Help decode the output of the python code
DC, first, third
Plot of
DC+a_1*sin(x)+a_3*sin(3x)