On the 14th of July students from the Last school, Auroville visited STEMLAND. The forty students accompanied by the teachers enjoyed their afternoon session by exploring STEMLAND.
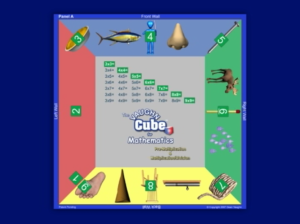
The arrangements were done by the STEMLAND team. There were 8 stalls which include
- Mindstorms
- Games and puzzles
- Science projects
- Makey-Makey
- Arduino
- Electronics
- Scratch programming
- 3-D printing.
Mindstorms:
Mindstorms is a hardware and software structure that develops programmable robots based on Lego building blocks. Each version includes computer Lego bricks, a set of modular sensors and motors, and Lego parts from the Technic line to create the mechanical systems. The system is controlled by the Lego bricks.
Games and puzzles:
Logic and strategy games were present. They include Abalone, Gobblet, Quads magnetic, Aadu Puli (Puli Meka), Linja, Quarto, Quoridor, Othello and Eternals were put on view to play. Puzzles like Rubik’s cube, Cast puzzles, and holograms were displayed to solve and play with.
Science Projects:
Science projects based on concepts were exhibited. The exhibits include
- Magnetic levitation
- Electromagnetism
- Acid-base indicator
- Dc electric motor model
- Crank’s model
- Lungs- diaphragm model
- Magnetism- properties.
- DIY microscope
- DIY headphone
- Series and parallel connection
- Lights color – arithmetic model.
These models were made using the Arvind Gupta toys which are made of scrap materials.
Makey – Makey:
Makey Makey is an invention kit by the MIT media lab. With Makey Makey, everyday objects are transformed into touchpads empowering students to interact with computers as creative tools. The computer becomes an extension of their creativity, fostering imaginative play and discovery.
“Makey Makey” is a play on words – students having the ability to Make their Keyboards (“Ma-Key”). The mundane and boring keyboard is replaced by any object that conducts electricity – pie pans, Play-Doh, bananas, and even potted plants – the list goes on.
The projects can be coded by scratch and use the Makey Makey kit as a joystick controller.
Arduino:
Arduino is an open-source hardware and software that can be used for designs. It is a microcontroller and microcontroller kit for building digital devices. It can be programmed and built using the Arduino software. Exhibits include a Distance measurement kit, Automated street light was displayed.
Electronics:
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behavior, and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Projects like Automatic street light controller and automated sound sensor control model, Automatic dustbin were displayed.
Scratch programming:
Scratch is a visual programming language that allows students to create their own interactive stories, games, and animations. As students design Scratch projects, they learn to think creatively, reason systematically, and work collaboratively.
3-D printing:
A machine allows the creation of a physical object from a three-dimensional digital model, typically by laying down many thin layers of a material in succession. The models are designed using software called Tinkercad and converted to the printing g code to feed to the machine using Ultimaker CURA software. This paves for creative models.
The visit session was facilitated by Dr.Sanjeev Ranganathan and the team of STEMLAND. The session started with a few minutes of concentration meditation and a few words about what we stand for, a casual talk on the similarities and differences between the last school and STEMLAND. Students had to choose any two stalls they can spend time on. Some of them wanted to explore all the activities.
Students and facilitators had a great time exploring. Few of them made hands-on projects using the kits provided. They played strategic games and got fascinated by them. It was a pleasure to have them in STEMLAND. The team had wonderful learning, growth, and fun having them.